Recycling Lives Services: Blazing A Trail in Liable Recycling
Recycling Lives Services: Blazing A Trail in Liable Recycling
Blog Article
Exploring Various Kinds Of Waste in Modern Waste Monitoring Systems
The contemporary landscape of waste management involves navigating an intricate selection of waste kinds, each needing specialized handling and disposal techniques to mitigate ecological influences. Municipal solid waste, dangerous waste, digital waste, and organic waste each existing unique challenges and chances for resource healing. Ingenious remedies such as smart waste containers and waste-to-energy innovations are arising as critical tools in boosting performance and sustainability. Understanding these waste kinds is essential for promoting public understanding and motivating active involvement in sustainable techniques. What strategies can efficiently address these diverse sorts of waste while advertising a round economy?
Municipal Solid Waste
Community solid waste, typically described as house garbage or waste, includes a variety of discarded materials produced by residential, business, and institutional sources within a municipality. This waste stream commonly includes items such as product packaging, food scraps, yard trimmings, paper, plastics, fabrics, and discarded family items. The administration of local strong waste is a vital part of metropolitan planning and public wellness, demanding reliable collection, transportation, and disposal systems.
Effective waste monitoring systems are designed to lessen environmental influence while taking full advantage of resource healing. This typically involves a combination of techniques including recycling, landfilling, and composting. Recycling programs target materials like paper, glass, steels, and certain plastics, diverting them from garbage dumps and reestablishing them right into the production cycle. Composting natural waste, such as food scraps and lawn trimmings, not just decreases landfill use but also generates beneficial dirt changes.
Districts should additionally deal with the economic and logistical obstacles associated with waste administration. Carrying out pay-as-you-throw systems, boosting public awareness, and buying innovation can substantially enhance waste diversion rates. By integrating these methods, districts can cultivate lasting areas, minimize greenhouse gas emissions, and preserve natural sources.
Contaminated Materials

Reliable dangerous waste management entails a number of important steps: identification, segregation, treatment, and disposal. Partition ensures that unsafe products are kept independently from non-hazardous waste to prevent cross-contamination.
Regulatory structures, such as the Resource Conservation and Healing Act (RCRA) in the USA, supply guidelines and criteria for contaminated materials monitoring. Adherence to these policies, coupled with developments in waste therapy innovations, is important in reducing the threats related to contaminated materials.
Electronic Waste
Electronic waste, typically referred to as e-waste, stands for a quickly expanding challenge in waste management systems worldwide. This kind of waste incorporates disposed of digital tools and tools such as mobile phones, computers, televisions, and other electronic devices. The quick pace of technical development, paired with decreasing item life expectancies and customer demand for the current tools, has greatly boosted the volume of e-waste created yearly.
E-waste is specifically problematic as a result of its complex composition, frequently consisting of hazardous pop over here substances like cadmium, mercury, and lead, which pose significant environmental and wellness threats if not appropriately taken care of. Conversely, e-waste likewise includes important materials such as copper, silver, and gold, which can be recovered and recycled. The twin nature of e-waste-- both unsafe and useful-- necessitates customized handling, reusing, and disposal processes.
Effective e-waste management entails rigorous governing frameworks, robust collection systems, and progressed recycling innovations. Public recognition and participation are critical, as incorrect disposal methods, such as prohibited dumping and informal recycling, aggravate environmental contamination and carcinogen. Improving e-waste administration methods is essential for reducing ecological influence and recouping important resources in a progressively electronic world.
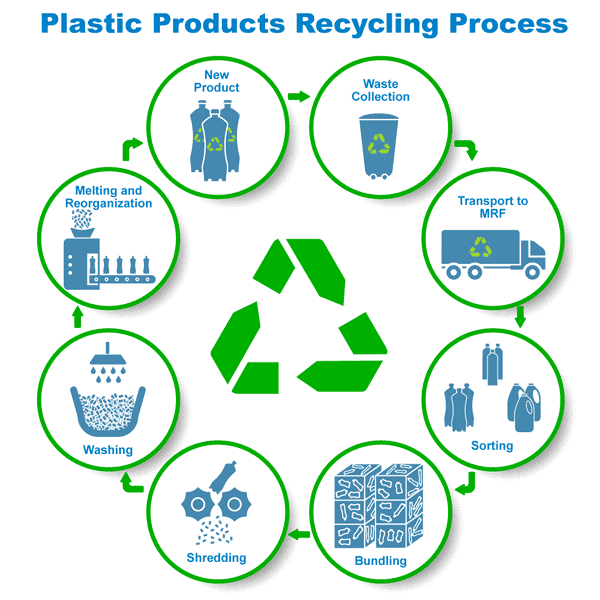
Organic Waste
Organic waste, comprising kitchen scraps, backyard trimmings, and farming deposits, represents a considerable part of the international waste stream. This kind of waste is naturally degradable, suggesting it can be damaged down by bacteria right into simpler organic substances. In spite of its potential for natural decomposition, improper monitoring of natural waste can result in adverse environmental effects, consisting of the discharge of greenhouse gases such as methane, which add to environment modification.
Reliable management of organic waste is important for lessening these environmental influences (recycling lives services). Composting additional resources is an extensively taken on technique, changing organic waste into nutrient-rich compost that can improve dirt wellness and farming efficiency. Additionally, anaerobic digestion is an emerging innovation that transforms natural waste right into biogas, a renewable resource source, and digestate, which can be made use of as fertilizer
Municipalities and waste administration entities must apply robust natural waste collection and therapy programs to make the most of the benefits of these procedures. Public education and learning campaigns can additionally play a pivotal function in motivating families and organizations to different natural waste from various other kinds of waste. By focusing on the management of natural waste, cultures can lower garbage dump use, lower greenhouse gas exhausts, and create valuable results for agricultural use.

Innovative Waste Administration
In the realm of waste management, cutting-edge techniques are changing how cultures manage their refuse, intending for sustainability and efficiency. One popular development is the implementation of wise waste bins equipped with sensing units that monitor fill levels and maximize collection routes.
Another notable development is the fostering of waste-to-energy (WtE) innovations. By transforming non-recyclable waste right into useful power via procedures such as incineration and anaerobic food digestion, WtE lowers garbage dump worry and provides a sustainable energy source. Innovations in chemical reusing allow for the malfunction of complex plastics into their original monomers, making it possible for the production of new, high-grade plastic items.
Additionally, the round economic situation design is getting traction, stressing the design of products and systems that prioritize reusability and resource efficiency. This all natural strategy encourages sectors to decrease waste generation from the beginning. Via these ingenious techniques, modern waste management systems are not just addressing the check immediate challenges of waste disposal however additionally leading the way for a much more lasting future.
Final Thought
A detailed understanding of metropolitan solid waste, unsafe waste, digital waste, and natural waste, coupled with the implementation of cutting-edge waste administration options, is critical for mitigating environmental impacts. Integrating innovations such as clever waste containers and waste-to-energy systems can enhance efficiency and sustainability. Reliable waste monitoring methods not just foster resource healing but likewise promote public recognition and involvement, eventually adding to the advancement of a circular economic situation.
The modern landscape of waste administration includes navigating a complicated selection of waste kinds, each needing specialized handling and disposal methods to reduce ecological influences. Community solid waste, unsafe waste, digital waste, and natural waste each existing distinct difficulties and opportunities for resource healing.Digital waste, generally referred to as e-waste, represents a rapidly expanding difficulty in waste monitoring systems internationally. Through these ingenious approaches, contemporary waste administration systems are not just resolving the prompt difficulties of waste disposal but also leading the way for an extra lasting future.
A detailed understanding of municipal strong waste, harmful waste, electronic waste, and natural waste, paired with the execution of innovative waste management services, is necessary for mitigating environmental impacts. (recycling lives services)
Report this page